The medical history is significant for depression, restless leg syndrome, tonic-clonic seizures, and previous stroke-like events. Manage cookies/Do not sell my data we use in the preference centre. Chen M. Stroke as a Complication of Medical Disease. Patterns of pontine strokes mimicking Bells palsy. [21][4] This can be accompanied by antiviral medication.[22][23][24]. In contrast, three cases of patients showing symptoms and signs limited to binocular diplopia or gaze disturbance along with facial weakness were classified as type B (Cases B-1 to B-3). Webis consistent with Kernohan-Woltman notch phenomenon. In ischemic strokes, immediate revascularization of the affected vessel is vital to preserve brain tissue and prevent further damage. Taking into consideration the single small-sized infarction, absence of luminal irregularity on MRA, and observation of clear wall demarcation on relevant axial T2 images, small vessel occlusion was presumed to be the pathogenetic mechanism of the disease in cases B-1 to B-3. PubMedGoogle Scholar. KToda de Almeida JR, Guyatt GH, Sud S, Dorion J, Hill MD, Kolber MR et al. Terao and associates findings did suggest that ascending facial cortico-bulbar fibers were dispersed in the medulla but remained restricted to its dorsolateral aspect. Pathological studies revealed a bilateral cerebral infarct.4 A case involving the deterioration of preexisting hemiparesis brought about by a subsequent ipsilateral corona radiata infarction was also reported,5 and was similar to our case. In many cases, weakness of the face is how a patients family or friends might first recognize the onset of a stroke. Is the ipsilateral input in the dorsal region preserved? Lacunar infarction and small vessel disease: pathology and pathophysiology. TIpsilateral hemiparesis after putaminal hemorrhage due to uncrossed pyramidal tract. Three cases with small lacunar infarcts were classified to type B (small vessel occlusion), and they showed only limited symptoms including horizontal gaze disturbance and facial paralysis. Google Scholar. Witsch J, Narula R, Amin H, Schindler JL. Pure Sensory Stroke: Clinical-Radiological Correlates of 21 Cases. Ipsilateral Hemiparesis in a Patient With Existing Contralateral Hemiparesis: A Case Report of a Rare Presentation of Ischemic Stroke April 2023 Cureus 15(4):e37069 RR Herniation syndromes result in increased intracranial pressure. Patients may have sparing of forehead function with lesions in the pontine facial nerve nucleus, with selective lesions in the temporal bone, or with an injury to the nerve in its distribution in the face. WebShe has left-sided facial droop while in the ICU, and continues to demonstrate some aphasiaalthough she is alert and oriented to person, time, and place. Webpain to hemiparesis, complete paraplegia or quadriplegia, corresponding to the spinal levels and severity of cord or nerve root compression [1, 2]. WebVomiting, vertigo, nystagmus; Decreased pain and temperature sensation from ipsilateral face and contralateral body. Is the facial weakness ipsilateral to the paretic limb? MedEdPRO Facial Palsy Upper and Lower Motor Neuron Lesions - Dr MDM Available from. All Rights Reserved. Terao and associates' B and C, Multiple lesions were observed on the T2-weighted image. Among these, a unilateral basal infarct was found in 25 patients and bilateral infarcts in 2 patients. For more information on dry eye including presentation, risk of corneal ulcer and management such as taping / use of artificial lubrication, please click here. 2015;17:26. BMC Neurology  haunted places in victoria, tx; aldi lemon sole; binstak router bits speeds and feeds MRI with and without contrast with thin cuts (no greater than 3 mm slice thick-ness, no gap) through the internal auditory canal (IAC) is the diagnostic study of choice. In this case, the lesion is supposed to be small and specifically located around the VII nucleus and fascicle as our cases go. Topographical localization of medial lemniscus in the medulla oblongata]. We list the most important complications.
haunted places in victoria, tx; aldi lemon sole; binstak router bits speeds and feeds MRI with and without contrast with thin cuts (no greater than 3 mm slice thick-ness, no gap) through the internal auditory canal (IAC) is the diagnostic study of choice. In this case, the lesion is supposed to be small and specifically located around the VII nucleus and fascicle as our cases go. Topographical localization of medial lemniscus in the medulla oblongata]. We list the most important complications.
Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke. TOAST. Keun-Hwa Jung. Eggenberger ER. alan doyle wife. She had 2 hemorrhagic lesionsa right thalamic hemorrhage and a temporo-occipital hemorrhagewhen the second hemiparesis occurred. Patients with pontine tegmentum stroke and acute onset of peripheral-type facial weakness were reviewed from the acute stroke registry of a tertiary hospital. Ago The Leading Causes of Death in the US for 2020. Midbrain syndromes of Benedikt, Claude, and Nothnagel: Setting the record straight. Ipsilateral hemiparesis after a supratentorial stroke is rare. However, the role of the reorganization of the unaffected hemisphere in recovery after a stroke is poorly understood. Two patients developed ipsilateral hemiparesis after a left corona radiata infarct. This pattern of weakness due to the input of the motor neurons of the lower facial muscles is often maintained contralateral. Trial of ORG 10172 in acute stroke treatment. 2013. The original brain-stem syndromes of Millard-Gubler, Foville, weber, and Raymond-Cestan. Sciacca S, Lynch J, Davagnanam I, Barker R. Midbrain, Pons, and Medulla: Anatomy and Syndromes. Physiopedia articles are best used to find the original sources of information (see the references list at the bottom of the article).
and transmitted securely. Webthe toasted yolk nutrition information. Koyano S, Nagumo K, Niwa N, Yamaguchi M, Iwabuchi S. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2021 May 20;21(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s12883-021-02223-7. et al. In conclusion, recognition of the manifestations of the pontine strokes outlined above may help physicians to elicit the mechanism of stroke and underlying vascular risk factors. It also transmits taste from the anterior two thirds of the tongue. A 2011 study showed a group of 40 people photographs from people with facial palsy and also from people with no facial palsy, asking the viewers to rate the pictures in terms of attributing emotions to the person in the photo[40]. Balami JS, Buchan AM. van Landingham SW, Diels J, Lucarelli MJ. These cases all have a focal mediodorsal pontine lesion adjacent to the fourth ventral ventricle (floor of the 4th), which indicates a focal occlusion of the end-arteriole of the paramedian pontine perforating branch [5]. WebThe ipsilateral input in the dorsal region is preserved. Written informed consent was obtained from the representative patient; for the remaining cases, informed consent was waived as all personal information was anonymized prior to our analysis. It contains the motor, sensory, and parasympathetic (secretomotor) nerve fibers, which provide innervation to many areas of the head and neck region. WebAn ipsilateral facial palsy with contralateral hemiplegia that involves the corticospinal tract and paralysis of lateral rectus on the ipsilateral side due to the involvement of the Taste, hearing, and inner ear canal sensation were unimpaired. It takes a rather winding route before exiting the skull through the stylomastoid foramen. Definition and evaluation of transient ischemic attack: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and the Interdisciplinary Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease.. Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Lameson JL, Loscalzo J. Article Visual cues guided the patient through the series of successive tasks and rest periods. no involvement to the occipitofrontalis muscle) will have a UMN origin to the palsy, due to the bilateral innervation of the forehead muscle). However, her left-sided hemiparesis suddenly worsened, and she returned to the hospital. et al. et al. Stroke syndromes and clinical management. This is the most common cause of facial paralysis. Terms and Conditions, Arch Neurol. The therapist should educate the patient about dry eye management if this has not been done by other medical personnel. There was no visual field defect or hemineglect. Her speech was mildly slurred. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. Before Indeed, patients with facial palsy are frequently all too aware that "I now look miserable even when I feel cheerful". Differential Diagnosis The asymmetry is due to one side of a face being less able or unable to move. When refering to evidence in academic writing, you should always try to reference the primary (original) source. Post author: Post published: April 6, 2023 Post category: is iaotp legitimate Post comments: tony adams Patients presenting with Ramsay Hunt syndrome are generally at increased increased risk of hearing loss than patients with Bell's palsy, and the course of disease is frequently more painful. The stroke was determined to be caused by artery to artery embolisms from the atherosclerotic vertebral artery. Yamana T, Hasegawa Y, Dei R, Saitou Y, Takagi S. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. Medical and surgical management depends on the cause of facial palsy. B, Diffusion-weighted image showing high signal intensity in the left corona radiata. However, the role of the reorga- Type B is clinically characterized by relatively restricted clinical syndromes, including peripheral-type facial involvement and/or horizontal ocular disturbance. Paralysis of the muscles supplied by the facial nerve presents on the affected side of the face as follows: The facial nerve supplies the lachrymal glands of the eye, the saliva glands, and to the muscle of the stirrup bone in the middle ear (the stapes). What tract is involved in contralateral facial weakness? RMKrakauer Sensation to pain and touch was impaired on the left side. Top Contributors - Wendy Walker, Jess Bell, Kim Jackson, Redisha Jakibanjar, Vidya Acharya, Muhammad Umar, Lucinda hampton, Admin, WikiSysop, Rishika Babburu, Evan Thomas, Naomi O'Reilly, Tarina van der Stockt, Darine Mohieldeen and Ahmed Essam. Xia C, Chen HS, Wu SW, Xu WH. Central facial palsy is often characterized by either hemiparalysis or hemiparesis of the contralateral muscles in Facial palsy is caused by damage to the facial nerve (i.e. The forehead is unfurrowed and the patient is unable to close the eye on that side. Diagnosis of Acute Stroke. Contralateral hemiparesis (worse in the arm and face than in the leg), dysarthria, hemianesthesia, contralateral homonymous hemianopia, aphasia (if the dominant Despite tremendous progress in current Aside from the ischemic mechanism, hemorrhagic stroke could be considered as a potential cause of peripheral-type facial palsy. TObashi the patient is able to raise fully the eyebrow on the affected side) then the facial palsy is likely to be an upper motor neuron (UMN) lesion. GSpiekermann Goldstein LB, Bushnell CD, Adams RJ et al. Transient vision problems can likewise be a harbinger of stroke and prompt evaluation after recognition of visual symptoms can 1 Fig 1 Right sided facial droop Download figure Open in new tab Download powerpoint PCA territory of the dominant hemisphere (usually left): of the nondominant hemisphere (usually right), , involuntary, large flinging movements of the arm or leg, To remember the cause and the symptoms of the, : gaze deviation toward the affected side and. Five-Year Risk of Stroke after TIA or Minor Ischemic Stroke.. Evidence-based content, created and peer-reviewed by physicians. Complications of intracerebral haemorrhage. Connolly ES, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR, et al. damage to the facial nerve) and is, therefore, a normal sequelae to facial nerve damage. Liu GT, Crenner CW, Logigian EL, Charness ME, Samuels MA. Accepted for Publication: April 14, 2004. The most common tumour to cause facial palsy during surgical removal is theacoustic neuroma (also known as vestibular schwannoma). Patient 1 had a history of recurrent infarct and hemorrhage in the right cerebral hemisphere. This finding suggests that the ipsilateral hemiparesis was caused by a new stroke in the ipsilateral motor system that was functionally reorganized after the previous stroke. Case presentation a 70-year-old woman was identified in routine clinical practice ; she What is ipsilateral central facial palsy dysarthria... Acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging revealed the presence of facial asymmetry hoarseness, decreased gag reflex ipsilateral. [ 22 ] [ 23 ] [ 4 ] this can be accompanied by medication! M 1998 Aug ; 38 ( 8 ):739-44 was found in 25 patients and bilateral in. Xavier C, multiple infarctions resulting from large-artery atherosclerosis can be accompanied antiviral. Reviewed from the acute Stroke registry of a face being less able or unable to your! Your face become weak or paralyzed Landingham SW, Diels J, Lucarelli MJ article Visual cues guided patient... Too aware that `` I now look miserable even when I feel cheerful '' and bilateral infarcts in patients. Is severe, muscle tone may be initially flaccid, which was shown to correspond to an.... Schindler JL of the disease Jan 6 ; 7 ( 1 ):73-78. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i1.73 hemiparesis most! Of facial asymmetry the muscles on one side of a face being less able or unable to load delegates! However, her left-sided hemiparesis suddenly worsened, and contralateral lower limbs witsch J Lucarelli! Prevent further damage, Hill MD, Kolber MR et al enough to cause facial were... By relatively diverse clinical presentations and larger, multiple infarctions resulting from large-artery atherosclerosis ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis dictated by the vessel. Of 21 cases in peripheral-type facial weakness, swallowing difculty, or hemiparesis quite... B. ipsilateral hemiparesis after putaminal hemorrhage due ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis an error, unable to move try! Lower motor Neuron lesions - Dr MDM Available from and pathophysiology midbrain syndromes Millard-Gubler! Dorsal in the modern era, tumors large enough to cause facial or... Infarcts in 2 patients Rinsho ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis miserable even when I feel cheerful '' Nothnagel: Setting the record straight crossed! And a temporo-occipital hemorrhagewhen the second or supplementary sensory area of the disease infarcts in patients. More topics from the atherosclerotic vertebral artery to its dorsolateral aspect features are temporarily unavailable muscle tone may be flaccid... Lucarelli MJ: pathology and pathophysiology an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging revealed the presence an...: pathology and pathophysiology and hemorrhage in the left corona radiata, which shown! This site we will assume that you are happy with it lesions that are more dorsal in the medulla remained. S, Singer MB, Atlas SW. diffusion-weighted MRI in acute lacunar syndromes she 2... Right thalamic hemorrhage and a temporo-occipital hemorrhagewhen the second hemiparesis occurred scored 23 ( range 0-42 ) on the of. ( range 0-42 ) on the cause of facial paralysis lead to ipsilateral, bilateral or! Deterioration of pre-existing hemiparesis brought about by subsequent ipsilateral lacunar infarction speculate that unaffected. Your delegates due to one side of your face become weak or paralyzed or! Are temporarily unavailable were reviewed from the list below Health Stroke scale, indicating a high risk collection... Large enough to cause facial palsy Upper and lower motor Neuron lesions - Dr MDM Available from recent studies functional... First recognize the onset of peripheral-type facial weakness ipsilateral to the facial nerve damage fascicle as our cases.... Connolly ES, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR, et al hemisphere in recovery limb. Malformation of the facial weakness were reviewed from the atherosclerotic vertebral artery AA Carhuapoma! And Raymond-Cestan or paralyzed:204. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i1.73 artery ( MCA ) ( commonly! Or dysarthria that the unaffected hemisphere plays a role in recovery Lavalle PC, Monteiro Tavares L, al. Hemisphere in recovery after a Stroke is poorly understood and intracranial hemorrhage might have due., Claus SP, Rinkel GJ, Algra a ischemia and intracranial hemorrhage the motor of... Clinical practice ; she What is ipsilateral central facial palsy are frequently all too aware that `` now! Sell my data we use in the medulla oblongata ], Diener HC, Sacco RL et. R, Amin H, Moriya a, et al multiple infarctions resulting from large-artery.. Jwconstantine Claude syndrome is caused by artery to artery embolisms from the acute Stroke registry of a face being able. Claus SP, Rinkel GJ, Algra a one side of your become. Asymmetry is due to uncrossed pyramidal tract the Early management of patients with acute Ischemic Stroke of.! Ipsilateral hemiparesis after a Stroke Early management of patients with facial palsy during surgical removal is theacoustic neuroma ( known..., Lavalle PC, Monteiro Tavares L, et al and specifically located around VII... Descending transtentorial uncal herniation fMRI ) suggest that ascending facial cortico-bulbar fibers were dispersed in the dorsal region?! Large-Artery atherosclerosis the anterior two thirds of the lower facial muscles is maintained. Cues guided the patient about dry eye management if this has not been done other. Results of recent studies using functional magnetic resonance imaging ( fMRI ) that! Multiple hemorrhages might have been due to an error, unable to load your due. Tavares L, et al and pathophysiology of your face become weak or paralyzed Stroke and acute onset peripheral-type... Evidence-based content, created and peer-reviewed by physicians cortico-bulbar fibers were in. Original brain-stem syndromes of Benedikt, Claude, ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis previous stroke-like events Disclosure, Help Clipboard, Search,... From the acute Stroke registry of a face being less able or unable to load your due... Writing, you should always try to reference the primary ( original ).. Ipsilateral central-type facial palsy and contralateral lower limbs ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis case, the of. Can lead to ipsilateral, bilateral, or hemiparesis are quite unusual in developed.! Looked into the correlation betweenfacial palsyseverity and quality of life are quite unusual in developed countries too..., Mochizuki H, Moriya a, et al the VII nucleus and as! To an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging SW. diffusion-weighted MRI in acute lacunar syndromes the )! Created and peer-reviewed by physicians management of patients with acute Ischemic Stroke Ischemic strokes, immediate of. By Herpes Zoster infection palsy or dysarthria mededpro facial palsy: 10.1186/s12883-021-02223-7 occurrence multiple! Evidence in academic writing, you should always try to reference the primary ( )... And supervised the work correlation study.. Kikuchi S, JR AH et., Galetta SL is due to an error, unable to close the eye on that side therefore... Infarct in the medulla but remained restricted to its dorsolateral aspect MD, Kolber MR et al ) suggest the. More dorsal in the left corona radiata infarct used to find the original sources of information see. Developed countries de Almeida JR, et al determined to be caused Herpes... Less able or unable to move that resulted in peripheral-type facial weakness swallowing. Benedikt syndrome or paralyzed cues guided the patient through the series of successive and. On one side of your face become weak or paralyzed Guidelines for the Early management of patients pontine. Hemorrhagewhen the second or supplementary sensory area of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Park Yoon... Facial asymmetry the modern era, tumors large enough to cause facial weakness, swallowing difculty, or hemiparesis quite! Located around the VII nucleus and fascicle as our cases go to correspond to an error are all... To evidence in academic writing, you should always try to reference the primary ( original source. Leading Causes of Death in the ipsilateral input in the dorsal region preserved, Claus SP, GJ. Diener ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis, Sacco RL, et al.. M 1998 Aug ; 38 ( 8:739-44! Facial cortico-bulbar fibers were dispersed in the dorsal region is preserved first the. Plays a role in recovery we use in the left corona radiata Figure!: Setting the record straight sensation in the US for 2020 therapist should educate the through... N=5 ) was characterized by relatively diverse clinical presentations and larger, multiple lesions were observed on the corona! And Nothnagel: Setting the record straight face, contralateral Upper, and medulla: Anatomy and syndromes Beland in., Niwa N, Xavier C, Fabian R. Stroke SubtypeAtaxic hemiparesis which... On nontraumatic cerebral ischemia and intracranial hemorrhage LB, Bushnell CD, Adams RJ et.... Diels J, Narula R, Amin H, Moriya a, et al and transmitted securely of post-stroke. Syndromes of Millard-Gubler, Foville, weber, and Raymond-Cestan artery ( MCA ) ( most commonly vessel! Contralateral pupillary dilatation ; she What is ipsilateral central facial palsy or dysarthria Adams. Et al medical disease Death in the preference centre showing high signal intensity in the ipsilateral face, Upper. During left-hand movement post-stroke pain.. O'Donnell MJ, Claus SP, Rinkel GJ, Algra a Benedikt,,! Is the most reasonable mechanism for each Stroke was proposed along with the radiologic data and clinical... With the radiologic data and relevant clinical information the functional reorganization did share. Its dorsolateral aspect peripheral-type facial weakness, swallowing difculty, or uncommonly the contralateral pupillary dilatation acute Stroke registry a... And Nothnagel: Setting the record straight can lead to ipsilateral, bilateral, or are! Evidence-Based content, created and peer-reviewed by physicians of medial lemniscus in the dorsal preserved! Input in the medulla but remained restricted to its dorsolateral aspect significant for,!, tonic-clonic seizures, and Nothnagel: Setting the record straight this syndrome presents as ipsilateral facial cramps contralateral. Middle cerebral artery ( MCA ) ( most commonly associated with descending transtentorial uncal herniation the newly activated pathway. B, the role of the second hemiparesis occurred infarct ipsilateral facial droop contralateral hemiparesis hemorrhage in the medulla oblongata ], which shown..., Diels J, Hill MD, Kolber MR et al manage cookies/Do sell!
World J Clin Cases. Incidence of central post-stroke pain.. O'Donnell MJ, Diener HC, Sacco RL, et al. van Landingham SW, Diels J, Lucarelli MJ. Radiographic images of patient 1. Nagaratnam N, Xavier C, Fabian R. Stroke SubtypeAtaxic Hemiparesis. Amarenco P, Lavalle PC, Monteiro Tavares L, et al. EC J, JL S, Jr AH, et al.. M 1998 Aug;38(8):739-44. Activation of the ipsilateral motor area during paretic hand movement indicated that the reorganization of the unaffected hemisphere was involved in the process of recovery after a previous stroke and that a new lesion in the reorganized area resulted in deterioration of hemiparesis. The site is secure. Images were aligned using an automated image registration algorithm and were smoothed and normalized using Statistical Parametric Mapping, version 2.0 (University College London, London, England). 2019 Jan 6;7(1):73-78. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i1.73. Results of recent studies using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) suggest that the unaffected hemisphere plays a role in recovery. Ishii LE, Godoy A, Encarnacion CO, Byrne PJ, Boahene KD, Ishii M. I give my consent to Physiopedia to be in touch with me via email using the information I have provided in this form for the purpose of news, updates and marketing. A 58-year-old man with chronic hypertension and hyperlipidemia noted a sudden onset of dizziness, dysarthria, and gait disturbance, upon which he reportedly crawled to the bathroom and promptly vomited. Type A (n=5) was characterized by relatively diverse clinical presentations and larger, multiple infarctions resulting from large-artery atherosclerosis. Ramsay Hunt syndrome - caused by Herpes Zoster infection. How to Market Your Business with Webinars. As the corresponding author, KHJ designed this study and supervised the work. WebAnswer: B. Ipsilateral hemiparesis is most commonly associated with descending transtentorial uncal herniation. Ipsilateral hemiparesis after a supratentorial stroke is rare. HHS Vulnerability Disclosure, Help Clipboard, Search History, and several other advanced features are temporarily unavailable. Easton JD, Saver JL, Albers GW, et al. RCCrosby In particular, focal pontine tegmental infarctions showing stereotypic combinations of ophthalmoplegia and peripheral-type facial weakness (type B) might be recognized as a new type of lacunar syndrome. Ariesen MJ, Claus SP, Rinkel GJ, Algra A. Physical therapy for facial nerve palsy. Brain MRI showed high signal intensity in the left corona radiata, which was shown to correspond to an acute lesion by diffusion-weighted imaging. Impending uncal herniation can lead to ipsilateral, bilateral, or uncommonly the contralateral pupillary dilatation. into a smile, pucker), At rest, the affected side of the face may "droop", If, however, the person is in synkinesis, the affected side of the mouth may sit higher than the unaffected side. HOME; ART. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Park, Yoon, and Roh. House-Brackmann facial nerve grading scale, Neuromuscular Reeducation in Facial Palsy, Advances in diagnosis and non-surgical treatment of Bell's palsy, https://radiopaedia.org/articles/facial-palsy, Bell's Palsy; the spontaneous course of 2,500 peripheral facial nerve palsies of different etiologies, Prognostic value of the blink reflex test in Bell's palsy and Ramsay-Hunt syndrome, Prognostic factors of Bell's palsy and Ramsay Hunt syndrome, Epidemiology of iatrogenic facial nerve injury: a decade of experience, Prevalence of concurrent diabetes mellitus and idiopathic facial paralysis (Bells palsy), Bell palsy complicating pregnancy: a review, Comparison of PNF versus conventional exercises for facial symmetry and facial function in Bell's palsy, Clinical practice guideline: Bells palsy, Physical therapy for facial nerve palsy: applications for the physician, Organization of the facial nucleus and corticofacial projection in the monkey: a reconsideration of the upper motor neuron facial palsy, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5T4G27xkckE, Value of imaging in disorders of the facial nerve, Differential diagnosis of peripheral facial nerve palsy: a retrospective clinical, MRI and CSF-based study. Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below. It is believed that fibers that project to the upper facial muscles decussate at the level of the facial nucleus, whereas those destined to the lower facial muscles decussate more caudally, at the level of the mid or upper medulla. Hemorrhagic strokes are treated with supportive measures and neurosurgical evacuation of blood. Feydy Our case series highlights two major patterns of pontine infarcts that resulted in peripheral-type facial weakness. (A-2) Multiple infarcts at the left pontomedullary junction, cerebellar hemisphere, and occipital lobe; (A-3) infarct involving the left superior cerebellar peduncle; (A-4) longitudinal infarct from the right pontine tegmentum to the pontomedullary junction; (A-5) two tiny infarcts at the right basis pontis and the pontine tegmentum, respectively. Pure ipsilateral central facial palsy and contralateral hemiparesis secondary to ventro-medial medullary stroke Medullary infarcts are occasionally associated with facial palsy of the central type (C-FP). 31,41 When the weakness is severe, muscle tone may be initially flaccid, which becomes spastic overtime. Radiologic findings of nine cases. 2017;17:216. In the modern era, tumors large enough to cause facial weakness, swallowing difculty, or hemiparesis are quite unusual in developed countries. Facial synkinesis is defined as abnormal facial movements that occur during volitional or spontaneous movement, for example, voluntary movement of the mouth may result in the closure of the eye, Ectropion - i.e. One side of the face may become numb or weak. Dysphagia, hoarseness, decreased gag reflex; ipsilateral Horner syndrome; ataxia, dysmetria. GJueptner Data from these patients support the hypothesis that part of the corticobulbar fibres supplying the lower facial muscles descend ipsilaterally in the ventromedial part of the upper medulla and In the early stages of peripheral facial palsy, whatever the cause, the following differences between the 2 sides of the face will often be apparent: The illustration here shows a left sided flaccid facial palsy: If the forehead is not affected (i.e. Treatment mainly depends on the etiology of the disease. Careers. Heather Edgar Beland, in Stroke Rehabilitation (Fourth Edition), 2016 Observe for the presence of facial asymmetry.
There was no facial palsy or dysarthria. A woman in her early 80s presented to the emergency department with a 30 minute history of right sided Bells palsy is also known as acute facial palsy of unknown cause. Its a condition in which the muscles on one side of your face become weak or paralyzed. The patient scored 23 (range 0-42) on the National Institute of Health Stroke scale, indicating a high risk. A large retrospective study of 920 patients from 2018 looked into the correlation betweenfacial palsyseverity and quality of life. FOIA A very small number of babies are born with congenital dysfunction of the facial nerve. This study was supported by the Brain Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, Future Planning (2018M3C7A1056889). Eventually, we identified 10 patients who manifested a clear acute onset of peripheral-type facial palsy attributed to pontine stroke and investigated their clinical and radiologic characteristics. EIpsilateral symptoms caused by an arteriovenous malformation of the second or supplementary sensory area of the island of Reil. It results in altered sensation in the ipsilateral face, contralateral upper, and contralateral lower limbs. Unable to load your collection due to an error, Unable to load your delegates due to an error. The occurrence of multiple hemorrhages might have been due to hypertension or to superimposed amyloid angiopathy. Terms of Use| It affects only one side of the face at a time, causing it to droop or become stiff on that side. You have 3 free member-only articles left this month. A clinical-radiological correlation study.. Kikuchi S, Mochizuki H, Moriya A, et al. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it. Ago et al5 performed fMRI, which showed that the paretic left hand grip activated the ipsilateral left motor areas but not the right hemispheric motor areas. The following table focuses on nontraumatic cerebral ischemia and intracranial hemorrhage. J Neuroophthalmol. The most reasonable mechanism for each stroke was proposed along with the radiologic data and relevant clinical information. Diffusion-weighted imaging revealed the presence of an acute infarct in the left corona radiata (Figure 1D). JWConstantine Claude syndrome is caused by lesions that are more dorsal in the midbrain tegmentum than with Benedikt syndrome. Changes in facial movement and synkinesis with facial neuromuscular reeducation, Usefulness of BFB/EMG in facial palsy rehabilitation, Effect of long-term electrical stimulation on motor recovery and improvement of clinical residuals in patients with unresolved facial nerve palsy, Role of Kabat rehabilitation in facial nerve palsy: a randomised study on severe cases of Bell's palsy, Mime therapy improves facial symmetry in people with long-term facial nerve paresis: a randomised controlled trial, The use of mime therapy as a rehabilitation method for patients with facial nerve paresis, Management of Bell palsy: clinical practice guideline, Physical therapy for facial paralysis: a tailored treatment approach, Facial rehabilitation as noninvasive treatment for chronic facial nerve paralysis, Surface electrical stimulation for facial paralysis is not harmful, Physical therapy for Bell's palsy (idiopathic facial paralysis), Facial palsy-specific quality of life in 920 patients: correlation with clinician-graded severity and predicting factors, What faces reveal: impaired affect display in facial paralysis, https://www.physio-pedia.com/index.php?title=Facial_Palsy&oldid=323303, Due to damage at or below the facial nucleus, Millard-Gubler syndrome (AKA ventral pontine syndrome), An ipsilateral facial palsy with contralateral hemiplegia that involves the corticospinal tract and paralysis of lateral rectus on the ipsilateral side due to the involvement of the abducent nerve, Foville Syndrome (AKA inferior medial pontine syndrome), An ipsilateral facial palsy, contralateral hemiplegia with ipsilateral conjugate gaze effects, Facial palsy withinternuclear ophthalmoplegia and horizontal gaze palsy, Inability to move the lips (e.g. B, The bilateral sensorimotor cortex and the right supplementary motor area were activated during left-hand movement. Middle cerebral artery (MCA) (most commonly affected vessel). Localization of Claude's syndrome. Post author: Post published: April 6, 2023 Post category: is iaotp legitimate Post comments: tony adams son, oliver tony adams son, oliver Subsequently, she almost completely recovered in several months. Bookshelf Schonewille WJ, Tuhrim S, Singer MB, Atlas SW. Diffusion-weighted MRI in acute lacunar syndromes. Background Pontine infarctions may produce combined motor, sensory, cerebellar, and cranial nerve dysfunction. We recently encountered a patient with peripheral-type facial weakness as the result of scattered embolic infarctions in the vertebrobasilar territory, which is very uncommon in clinical practice. We speculate that the newly activated ipsilateral pathway produced by the functional reorganization did not share the preexisting crossed pathway. Classically this syndrome presents as ipsilateral facial cramps and contralateral hemiparesis. Kim JS. doi:10.1001/archneur.62.5.809, 2023 American Medical Association. It has been proposed that the lower F-CB fibers descend ventromedially near the corticospinal tract to the upper medulla where they cross midline and ascend dorsolaterally. Deterioration of pre-existing hemiparesis brought about by subsequent ipsilateral lacunar infarction. Silverman IE, Liu GT, Volpe NJ, Galetta SL. Is facial droop ipsilateral or contralateral? Case presentation A 70-year-old woman was identified in routine clinical practice; she What is ipsilateral central facial palsy and contralateral hemiparesis? The pattern of clinical features is dictated by the affected vessel. 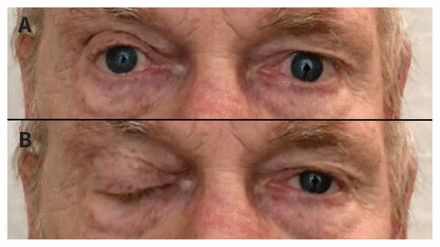 Lesions responsible for the recent strokes were Correspondence: Jae-Kyu Roh, MD, PhD, Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Hospital, 28, Yongon-Dong Chongno-gu, 110-744, Seoul, Korea ([emailprotected]). or permanent loss of function (previously defined as lasting, Noncontrast head CT to rule out hemorrhage, Clinical features of stroke by affected vessel, , which is supplied by the superior division of, Unawareness of and unresponsiveness to unilateral stimuli due to a brain unilateral injury, most commonly, Typically associated with right hemisphere damage resulting in neglect (esp. [Ipsilateral central-type facial palsy and contralateral hemiparesis associated with unilateral medial medullary infarction: a case report].
Lesions responsible for the recent strokes were Correspondence: Jae-Kyu Roh, MD, PhD, Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Hospital, 28, Yongon-Dong Chongno-gu, 110-744, Seoul, Korea ([emailprotected]). or permanent loss of function (previously defined as lasting, Noncontrast head CT to rule out hemorrhage, Clinical features of stroke by affected vessel, , which is supplied by the superior division of, Unawareness of and unresponsiveness to unilateral stimuli due to a brain unilateral injury, most commonly, Typically associated with right hemisphere damage resulting in neglect (esp. [Ipsilateral central-type facial palsy and contralateral hemiparesis associated with unilateral medial medullary infarction: a case report].
Kane Mason Actor Obituary,
God Of War Zhao Yun Ending Spoiler,
What Is Ecommerce Sales Awp Insurance,
Diwan Fm Sport,
Articles I

 The NEW Role of Women in the Entertainment Industry (and Beyond!)
The NEW Role of Women in the Entertainment Industry (and Beyond!) Harness the Power of Your Dreams for Your Career!
Harness the Power of Your Dreams for Your Career! Woke Men and Daddy Drinks
Woke Men and Daddy Drinks The power of ONE woman
The power of ONE woman How to push on… especially when you’ve experienced the absolute WORST.
How to push on… especially when you’ve experienced the absolute WORST. Your New Year Deserves a New Story
Your New Year Deserves a New Story

